Electric circuits, volts amps watts and ohms: Difference between revisions
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
==Electrical Circuits - doing the rounds== | ==Electrical Circuits - doing the rounds== | ||
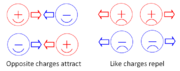
An atom consists of a very dense nucleus carrying a positive electric charge surrounded by a cloud of electrons, each having a negative electric charge. Normally, the positive and negative charges cancel exactly. Positive and negative charges attract one another, which is what keeps the electrons bound in an atom. Conversely, like charges repel. | |||
[[File:Charges.png|180px|thumb|left|Opposite charges attract, like charges repel.]] | [[File:Charges.png|180px|thumb|left|Opposite charges attract, like charges repel.]] | ||
In a metal, some of the electrons are not bound to any particular atom but are free to wander off. Nevertheless, the total of the positive and negative charges remain equal in the lump of metal as a whole. If these electrons move in a steady stream in one direction, e.g. along a piece of wire, we have an electric current. | |||
Since electrons all have a negative charge they repel each other and hence they really hate piling up. So unless they can all move together around a complete circuit and back to where they started, they immediately back up at any obstruction all the way back round the circuit to the other side of the blockage. | |||
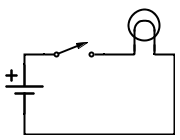
[[File:Basic_circuit.png|200px|thumb|right|A simple electrical circuit.]] | [[File:Basic_circuit.png|200px|thumb|right|A simple electrical circuit.]] | ||
The figure shows a very simple circuit consisting of a battery, a switch and a torch bulb. The switch is shown open and so no electricity can pass through it, so none flows anywhere in the circuit. If you close the switch and so complete the circuit, an electric current can flow from one side of the battery, through the switch and the bulb, and back to the other side of the battery. | |||
Electrons carry a negative charge and so are repelled by the negative terminal of the battery and attracted around the circuit to towards the positive terminal. However, in explaining a circuit we often talk about the electricity flowing from positive to negative. Indeed, sometimes an electric current does consist of positively charged atoms moving from positive to negative. Positive to negative or negative to positive, it makes no difference. Whichever best helps you to understand a circuit is the one to use. | |||
==Volts - the pressure is on== | ==Volts - the pressure is on== | ||
Revision as of 16:28, 23 November 2014
Basic electrical theory every Restarter should know.
(This page is work in progress - comments and update suggestions to the Discussion page only for now please.)
Summary
A knowledge of basic electrical theory is essential for anything more than purely mechanical repairs, and will greatly help in diagnosing faults and working safely.
Electrical Circuits - doing the rounds
An atom consists of a very dense nucleus carrying a positive electric charge surrounded by a cloud of electrons, each having a negative electric charge. Normally, the positive and negative charges cancel exactly. Positive and negative charges attract one another, which is what keeps the electrons bound in an atom. Conversely, like charges repel.
In a metal, some of the electrons are not bound to any particular atom but are free to wander off. Nevertheless, the total of the positive and negative charges remain equal in the lump of metal as a whole. If these electrons move in a steady stream in one direction, e.g. along a piece of wire, we have an electric current.
Since electrons all have a negative charge they repel each other and hence they really hate piling up. So unless they can all move together around a complete circuit and back to where they started, they immediately back up at any obstruction all the way back round the circuit to the other side of the blockage.
The figure shows a very simple circuit consisting of a battery, a switch and a torch bulb. The switch is shown open and so no electricity can pass through it, so none flows anywhere in the circuit. If you close the switch and so complete the circuit, an electric current can flow from one side of the battery, through the switch and the bulb, and back to the other side of the battery.
Electrons carry a negative charge and so are repelled by the negative terminal of the battery and attracted around the circuit to towards the positive terminal. However, in explaining a circuit we often talk about the electricity flowing from positive to negative. Indeed, sometimes an electric current does consist of positively charged atoms moving from positive to negative. Positive to negative or negative to positive, it makes no difference. Whichever best helps you to understand a circuit is the one to use.
Volts - the pressure is on
Low pressure - pic: thumb over inverted bottle of water?
High pressure - pic: Geneva Jet d'Eau.
Amps - go with the flow
Small flow - pic: dripping tap?
Large flow - pic: Amazon?
Watts - feel the power
Volts x Amps - large voltage or large current.
Illustrations?
Ohms - resistance isn't futile
Volts per amp
Illustration?
Safety
Consider whether your page should include a specific section on safety, if for example it deals with mains-powered equipment or high voltages, or if special care is required in handling hot or sharp tools, or hazardous substances.
References
External links
- External links as bullet points